ATTENTION STUDENTS WHO MISSED THURSDAY, APRIL 26TH'S CLASS:
YOUR ONE AND ONLY OPPORTUNITY TO WRITE THE MISSED QUIZ WILL BE AT 5:30PM, MAY 1ST, 2012 IN ROOM 20.
Friday, April 27, 2012
Thursday, April 26, 2012
Tuesday, April 24, 2012
Tuesday, April 24, 2012
Disorders of the Respiratory System:
· Common Cold and Influenza
o Increase in mucus in nasal cavity
o Change in colour of mucus
o Tickle in throat (decrease in mucus)
· Bronchitis
o Inflammation of the bronchi and bronchioles (virus)
o Shortness of breath, coughing, wheezing (due to narrowing of the air passageways)
o Mucus accumulates in the bronchi
o Short-term
· Bronchial Asthma
o Inflammation of the bronchi and bronchioles (allergic reaction)
o Chronic
o Shortness of breath, coughing, wheezing (due to narrowing of the air passageways)
o Regulated with inhaler
· Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
o Prevents carrying of oxygen in red blood cells by binding to haemoglobin
o Nausea, headaches, dizziness, loss of sensation, confusion, loss of consciousness, death
o Prevented with CO detector in house
Pg 223: #1-9
1) The main functions of the respiratory system are: taking in (inspiration) oxygen sufficient for cellular functions and breathing out (expiration) carbon dioxide
2) The respiratory system is related to the circulatory system because the respiratory system ‘feeds’ or supplies the circulatory system with oxygen and circulatory system heats incoming air of respiratory system.
3) We need to breath continuously because of high oxygen demand in humans and the quick reaction time of gas exchange.
4) Functions of:
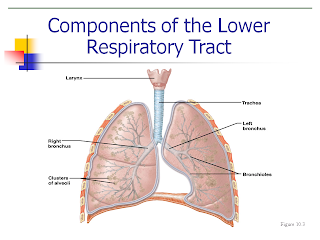
a. Epiglottis: directs air to the trachea
b. Trachea: transports air from pharynx to lungs
c. Cartilage rings of the trachea and bronchi: provides flexibility and rigidity to maintain open airway
d. Goblet cells: produce mucus (therefore trapping debris)
e. Cilia: air filter in nasal cavity
f. Alveoli: air sacs involved in gas exchange between air and blood via diffusion
5) Trace the path of an oxygen molecule in the air from the time it enters the body until the time it enters the bloodstream...see handout.
6) The larynx structure is two thin elastic ligaments (vocal cords)
The larynx function is to produce sound through vibrations created by air flow.
Larynx in males is generally larger (after puberty) and vibrates at lower frequencies.
7) Alveolus diagram: see back of handout.
8) Muscle actions for:
Inspiration: diaphragm contracts (moves downward) and intercostals muscles contract (move up and outward)
Expiration: diaphragm relaxes (moves upward) and intercostals muscles relax (move down and inward)
9) Compare frog and human respiratory system...see chart.
Advantage: for frogs is the gas exchange that occurs on their moist skin
Thursday, April 19, 2012
Thursday, April 19th, 2012
The Circulatory System
-read over section 3.9 and 3.10 being familiar with terms and previously assigned questions
-functions of the system
-structure (labelling components)
-understanding blood vessels and blood components
-be able to compare human and fish systems
The Respiratory System
-read over section 3.15 being familiar with terms and previously assigned questions
-function of the system
-structure (labelling components)
-how we breathe
-be able to compare human and frog
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)