UNIT TEST #2: MICROBIOLOGY
MULTIPLE CHOICE (1 mark each)
1.
The study of
genes and the inheritance of traits is:
a.
Heredity
b.
Offspring
c.
Genetics
d.
Fertilization
2.
The different versions of a characteristic are
considered:
a.
Genes
b.
Phenotypes
c.
Genotypes
d.
Traits
3.
The bits of information passed down from parent to
child are called:
a.
Offspring
b.
Fertilization
c.
Genes
d.
Reproduction
4.
A combination of alleles is:
a.
Genes
b.
Genotype
c.
Dominant
d.
Recessive
5.
Offspring of true-breeding plants are called:
a.
Mixed
b.
Heterozygous
c.
Homozygous
d.
Hybrid
6.
A heterozygous dominant genotype is correctly represented
with:
a.
GG
b.
Gg
c.
gG
d.
gg
7.
Ova and sperm are often called:
a.
Gametes
b.
Eggs
c.
Zygotes
d.
Reproduction
8.
This type of reproduction produces a genetically
identical offspring to the parent:
a.
Artificial Insemination
b.
Genetic Engineering
c.
In Vitro Fertilization
d.
Cloning
9.
If the letter B represents the gene for body colour
and blue is dominant to yellow, an individual with a yellow body would have the
genotype:
a.
BB
b.
Yb
c.
Yy
d.
bb
SHORT ANSWER
(2 marks each)
10. A one-eyed
purple people eater is crossed with a two eyed purple eater. All their offspring have two eyes. Which trait is dominant? Why?
Two eyes is dominant because all the offspring
must have Ee (producing the same phenotypes).
11. If you use
the letter E for this gene (from question #10), what are the genotypes of the
offspring? (hint: Punnett Square)
EE crossed with ee would give the same genotype
of Ee to all offspring and therefore the same phenotype (two eyes).
Ee crossed with ee would give half the offspring
Ee and the other half ee (two different phenotypes).
12. What is
cross-pollination of pea plants? Give an example.
Cross-pollination means that the seeds came from
two different plants. For example,
Mendel fertilized flowers by brushing pollen from the flower of yellow pea
plants and whipping the pollen on the carpel of green seed plants.
13. Use the
offspring in the F1 generation to self-pollinate to create the parents of the
F2 generation.
 |
|||
 |
|||
14. If tall
bodies are dominant over small bodies (question #13), than what are the chances
of:
a.
Child in F1 having a tall body?
4 out of 4 =
100%
b. Child in F2
having a tall body?
3 out of 4 =
75%
LONG ANSWER
(marks vary)
15. Label the
diagram below with the stages of meiosis II (4 marks):
16. Fill in the
blank with stage of meiosis I associated with the description (6 marks).
Stage
|
Description
|
Metaphase I
|
Homologous chromosomes are lined up side by side as
tetrads
|
Interphase I
|
The cell replicates its chromosomes
|
Anaphase I
|
Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite
ends of the cell
|
Prophase I
|
Homologous chromosomes come together matched gene by
gen forming a tetrad
|
Telophase I or Cytokinesis
|
The cytoplasm divides an yields two new cells
|
Prophase I
|
Crossing over occurs
|
17. Match the
following genetic disorders to their effects (put letter in blank, 5 marks):
a.
Down’s Syndrome
b.
Sickle Cell Anemia
c.
Klinefleter’s
d.
Turner’s
e.
Cystic Fibrosis
___b___ red blood cells become crescent shaped
___d___ under developed ovaries
___c___ development of breast tissue in males
___a___ some degree of mental retardation
___e___ fluid in lungs
18. Complete the
chart for sexual and
asexual reproduction (6 marks):
Sexual
|
Asexual
|
|
Offspring are produced from
|
From a single parent
|
From two sex cells
|
Associated cellular division process
|
Mitosis
|
Meiosis
|
Example
|
Strawberries (have runners), Hydra (have buds)
|
Animals (have testes and ova), Plants (have stamen and carpel)
|
UNIT TEST #3: MICROBIOLOGY
(40 marks total)
1.
Why do we use genus and species names and not common names (2
mark)?
We use the genus and species names because there are problems
using common names.
2.
Explain cell reproduction in the lytic cycle (text or labeled
diagram) (6 marks).
(1) Phage attaches to a specific host bacterium and (2) injects its DNA,
(3) disrupting the bacterial genome and killing the bacterium, and (4) taking
over the bacterial DNA and protein synthesis machinery to make phage parts. (5)
The process culminates with the assembly of new phage, and (6) the lysis of the
bacterial cell wall to release a hundred new copies of the input phage into the
environment.
3.
Bacteria are divided into two main groups (2 marks):
a.
Archeabacteria
b.
Eubacteria
4.
Name three types of microbes in our world (3 marks):
a.
Viruses
b.
Bacteria
c.
Protists
5.
What are the two main components of a virus (2 marks)?
a.
Protein capsid/coat
b.
Genetic information (DNA or RNA)
6.
Please complete the table below (4 marks):
Classification
|
Ecological
Role
|
Methanogens
|
-produce methane as a byproduct of
sewage treatment or landfill operation
|
Thermophiles
|
-contain genes for heat-stable
enzyme that may be of great value in industry and medicine
|
Cyanobacteria
|
-perform ‘modern photosynthesis’
converting water into oxygen
|
Halophiles
|
-ph0tosynthesize with
bacteriorhodopsin rather than chlorophyll
|
7.
Please complete the table below for any type of protist (2
marks):
Type
|
Example
|
Eco-logical Role
|
Plant-like
Animal-like
Fungi-like
|
Algae
Diatoms
Euglena
Amoeba
Paramecium
Plasmodium
Slime-mould
|
2/3 of world’s oxygen
Glass, road paint, toothpaste
Found in animals to help digest
cellulose
Cause of malaria
|
8.
List three ways you can prevent the spread of diseases caused
by microbes (3 marks):
a.
Use antibiotics correctly
b.
Get immunized
c.
use
care when preparing and handling food
d.
Keep surfaces clean and disinfected
e.
Wash
your hands
9.
Bacteria are/can: (circle all that apply) (5 marks)
unicellular
prokaryotic
have cell walls
heterotrophs
autotrophs
aerobic
anaerobic
live symbiotically
helpful
harmful
reproduce by conjugation
reproduce by binary
fission
spherical in shape
produce an endospore
identified with Gram stain
10. What are two ways drinking
water is purified (2 marks)?
a.
UV light
b.
Chlorination
11. Sketch a bacteriophage and
label five components in your diagram (7 marks).
12. What is a mycelium (2 marks)?
A network/aggregate of hyphae found
on fungi.
TEST #4: ANIMAL ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY


TEST #5: PLANT STRUCTURE & PHYSIOLOGY
TEST #4: ANIMAL ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
Human Physiology & Anatomy Unit
Test
(70 marks – 1 mark for showing up
today)
- Characteristics of life include (5 marks):
1.
Movement
2.
Responsiveness
3.
Growth
4.
Reproduction
5.
Respiration
6.
Digestion
7.
Absorption
8.
Circulation
9.
Assimilation
10.
Excretion
- Life depends on the availability of the following (5 marks):
1.
Water
2.
Food
3.
Oxygen
4.
Heat
5.
Pressure
- Identify two of the body sections below (2 marks):
Transverse Coronal Sagittal
- Label ten key components on the heart diagram (10 marks):
- List the functions of the Respiratory System (4 marks)
Overall Function:
· Gas
exchange with circulatory system
· -
Take in oxygen for cellular respiration: energy
· -
Release carbon dioxide: waste
Upper Functions:
· Passageway for respiration
· Receptors for smell
· Filters incoming air to filter larger foreign materials
· Moistens and warms the incoming air
Resonating
chamber for voice
Lower Functions:
· Larynx:
maintains an open airway, routes food and air appropriately, assists in sound
production
· Trachea:
transports air to and from lungs
· Bronchi:
branch into lungs
Lungs: transport air to alveoli
for gas exchange
- Please complete the blank with the appropriate component of the Respiratory System (9 marks).
______Nasal Cavity____ - Contains nasal septum, turbinates, and
cilia
____Pharynx___
- Throat; common passageway for air and food
____Epiglottis____
- When food is swallowed,
this closes over the opening to the larnyx, preventing food from entering the
lungs.
_____Larynx____
- Voice box. Triangular
chamber below pharynx. "Adam's Apple".
____Trachea_____
- Windpipe; walls are alternate bands of membrane and c-shaped rings of hyaline
cartilage to keep it open. Lined with ciliated mucous membrane. Coughing and
expectoration gets rid of dust-laden mucous.
_____Bronci___
- Similar to trachea with
ciliated mucous membrane and hyaline cartilage. Lower end of trachea divides
into right and left this.
_____Brochioles______
- Thinner walls of smooth muscle, lined with ciliated epithelium. Subdivision
of bronci. At the end, alveolar duct and cluster of alveoli.
____Alveoli__
- Composed of single
layer of epithelial tissue. Inner surfaces covered with surfactant to keep from
collapsing. Each surrounded by capillaries. Oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange
takes place between these and capillaries.
____Lungs___
- Fill thoracic cavity.
Tissue is porous and spongy- it floats.
- Define each term below (4 marks):
Ingestion: the
taking in of nutrients
Digestion: the
breakdown of complex organic molecules into smaller components by physical
and chemical means
Absorption: the
taking up of digested molecules into the cells of the digestive tract
Egestion: the
removal of waste food materials from the body
- Explain the process of excretion (use as many points as you wish)(5 marks):
·Blood travels to the kidneys
·Capillaries bring the blood to the Nephron
·In the Glomerulus (of the Nephron) water, salts, urea,
amino acids, and glucose are filtered into the Bowman's capsule.
·As the materials travel through the Proximal Tubule,
glucose, vitamins, sodium, amino acids, potassium and bicarbonate are
reabsorbed into the blood.
·In the Loop of Henle, water and salt are reabsorbed into
the blood
·In the Distal Tubule, ammonia, uric acid, penicillin, and
hydrogen ions are secreted into the collecting waste
·The material travels from down the Collecting Duct to the
Ureter.
·The urine reaches the Urinary Bladder where it is
temporarily stored.
·Urine is excreted from the bladder through the Urethra
with the aid of a Sphincter.
- Label the Digestive System (10 marks)
- Identify a kidney-related diseases and the symptoms (2 marks).
- The Central Nervous System is composed of (2 marks):
- Brain
- Spinal Cord
- Two types of neurons (2 marks):
·
Motor Neuron
·
Sensory Neuron
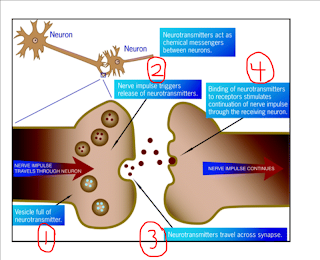
- Components of a neuron (5 marks):
- Describe the process of neurotransmission/synapses (4 marks):
TEST #5: PLANT STRUCTURE & PHYSIOLOGY
UNIT TEST
#5: Plant Physiology
(40
marks)
1.
For the life cycle below, fill in the five
boxes to complete the labeled diagram (5 marks).
·Sporophyte produces and releases asexual spores from within a
sporangium
·Spores germinate and develop into a small, heart shaped gametophyte
·Mature gametophyte produces egg and sperm
·Mature sperm cells are released and unit with eggs cells, producing
a zygote.
·Zygote develops into sporophyte
The cycle repeats
2.
Fill in the chart for 3 characteristics as they
help to identify Monocots vs. Dicots (6 marks).
|
Monocots
|
Dicots
|
|
Leaf venation is parallel |
Leaf venation is net-like |
|
Petals occur in 3s (3, 6, 9, 12) |
Usually have 4 or 5 petals |
|
Fibrous roots |
Tap root |
|
One cotyledon (seed leaf) |
Two cotyledons (seed leaves) |
|
Corn |
Bean |
3.
Label the following flowering
plant components (6 marks).
|
|
4.
Label ten of the following
plant components (10 marks).
5.
For each of the following types
of tissues, identify their main function
(4 marks).
Meristem: plant tissue composed of cells
that divide (mitosis) to allow for growth and cell differentiation into the
other three types of tissue systems in the plant
Ground: internal nonvascular tissues
involved in photosynthesis, support & storage of nutrients
Dermal: cells specialized for covering
the outer surface of the plant (leaves, stems & roots)
Vascular: internal vascular tissues
involved in transporting water and other substances among cells
6.
Identify the following types of
propagation (2 marks):
| Layerage & Budding | |||
7.
Identify three of the following
types of leaf arrangements (3 marks).
8.
For four of the components of
the leaf below, state their function (4 marks).
(a) cuticle & epidermis - prevents
water loss
(b) palisade mesophyll - photosynthesis
(c) stomata - gas exchange
(d) spongy mesophyll - gas exchange and
photosynthesis
(e) guard cells - regulates stomatal
openings